Approximately 1.4 million adults and children have Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis.
- Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis belong
to a group of conditions known as inflammatory
bowel diseases (IBD). These diseases
should not be confused with irritable bowel
syndrome (IBS), an unrelated condition that
is medically less serious. - Both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis
are chronic, or long-term, conditions. The
diseases are unpredictable and cyclical.
Most children who have ulcerative colitis
or Crohn’s disease go on to lead full and
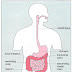
productive lives. - Crohn’s disease is a condition in which the
walls of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract become
irritated, inflamed, and swollen. This
inflammation can occur anywhere in the
GI tract, including the mouth, esophagus,
stomach, small intestine, large intestine
(colon), and rectum. See figure 1.
- Ulcerative colitis causes inflammation in the
large intestine, or colon, only. Tiny open sores
or ulcers form on the surface of the lining,
where they bleed and produce pus and mucus. - Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis may
occur in children of any age, but the usual
onset is between 15 and 25 years of age. - More recently, there has been a rise in the number
of elementary school age children diagnosed
with IBD. You should know that: - The illnesses are not contagious.
- Both conditions cause similar symptoms
including:- diarrhea (sometimes bloody)fatigue
- loss of appetite and weight loss
- crampy abdominal pain
- intense cramps that can come on without
- warning, creating sudden urges to use the
- bathroom. The urgency may be so great
- that it can result in fecal incontinence
- (accidental leakage of stool) if there is a
- delay in reaching the toilet.
- Some adolescents with IBD may have delays
in physical growth and puberty, causing
them to look younger and smaller than their
peers. Many children with these conditions
also have joint pain and skin rashes. - Some young people with Crohn’s disease or
ulcerative colitis have more chronic pain than
others. Chronic pain has been linked to numerous
school-related difficulties, including
frequent absences, decreased ability to
concentrate and perform academically, and
impaired ability to cope with the demands
of the classroom setting. - Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are
lifelong illnesses. Medications can alleviate
inflammation and discomfort, but are not
cures for the diseases. In addition, many of
the medications used cause unpleasant side
effects such as weight gain and mood swings. - Surgery may be an option if symptoms and
inflammation cannot be controlled by medication
alone.










0 comments:
Post a Comment